Introduction
SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) is an advanced master data management platform. It supports the central creation, modification and distribution of master data in your entire system landscape. It is also possible to consolidate all master data in the entire IT landscape.
SAP MDG is standard available for various domains as presented below.
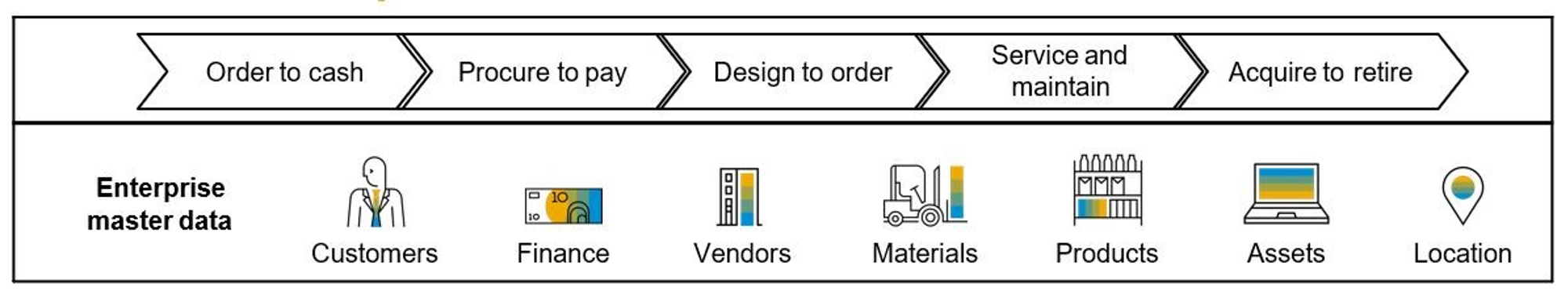
In this blog, we focus specifically on SAP Master Data Governance for Financials (MDG-F). SAP MDG-F is SAP's standard solution to centrally govern financial master data. It provides a centrally positioned application to manage and control master data, no matter whether the master data is processed locally or centrally. The financial master data can be created, completed and changed in the so-called staging area. In this staging area, the master data is not yet available for the underlying business applications. Only when the data has been checked, completed and approved, the master data will be made available for use. This solution can be used for a wide range of financial master data, such as controlling, charts of accounts, cost centres, general ledger accounts, and company numbers and controlling objects such as profit centres and cost centres with hierarchies. The MDG-F solution is available for end users via ABAP Web Dynpro and SAPUI5 (Fiori), which offers flexibility for changes according to the end user’s requirements.
Why MDG-F?
A problem that many companies are facing nowadays, is that a lot of information used for business operations is duplicated or incorrectly stored. For example, when a cost centre occurs several times in a system like "Alluvion" or "Alluvon", then there is a real chance that some bookings will be missing. Possible consequences of this are less profit, more costs or delayed payments.
Performing a good and reliable audit becomes a challenge with duplicated data in the system. It will take more time to analyze the audit and allocate the duplicated data, resulting in longer processing times and higher costs. Next to inefficiency, there is also an increased chance of incorrect reporting.
MDG-F is ideal for taking the quality and consistency of financial data to a higher level. It ensures consistent data between local and enterprise systems, with only one source and so only one truth. Data models are standardized, validation of data can be set up company-wide but also locally and workflows are available to guide request-, change- and approval processes. As a result, reliable information can easily be extracted from the system, data is consistent and data modelling, planning and analysis will improve.
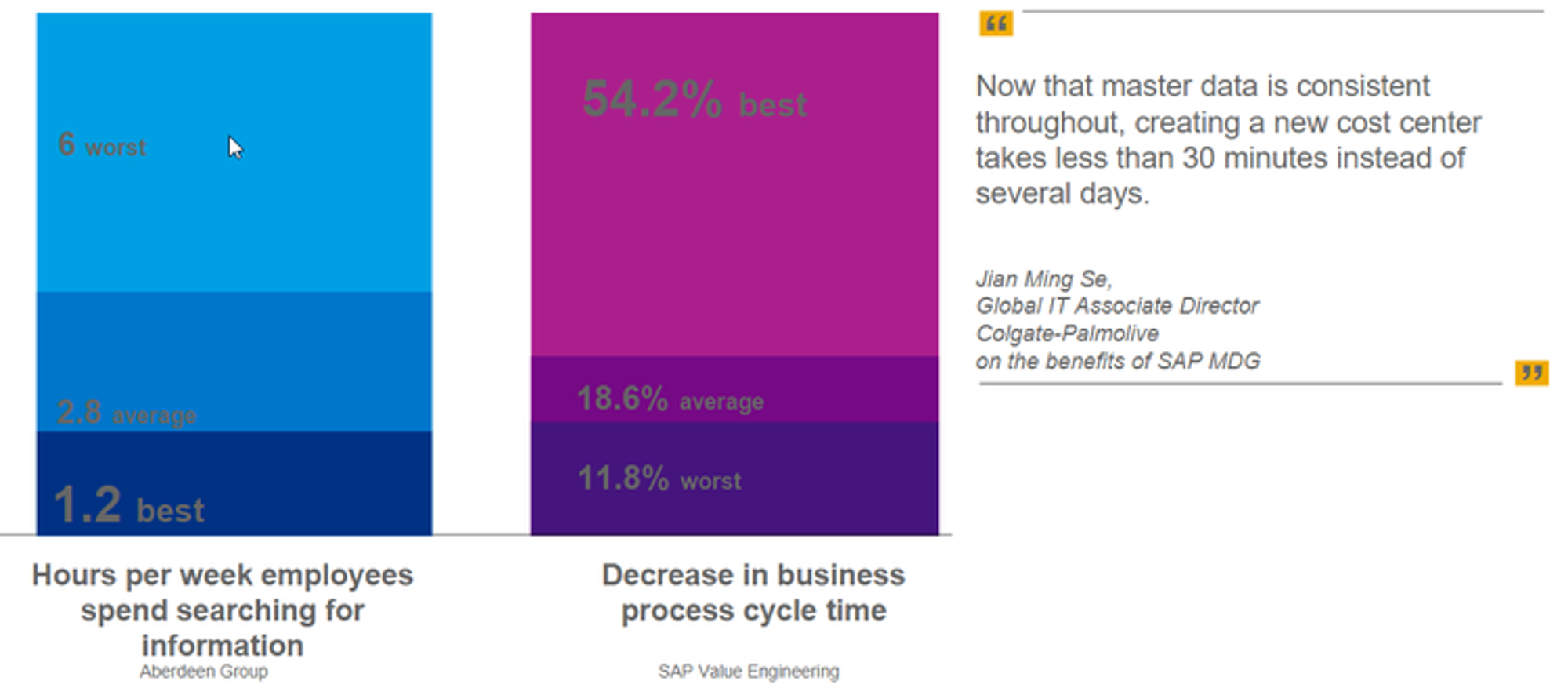
As regulations are increasing in complexity and keeping them up-to-date becomes a daily task, the option of streamlined and automated processes for complying with these regulations is a great advantage. It offers transparency, and traceability and eliminates the risks associated with non-compliance.
In this graph, you can see that there is a big difference between the best and worst regarding hours spent on searching for information and business process cycle time. If data is well managed, the difference will be smaller, making data more efficient and easier to find.
What is MDG-F?
As you can see in the hierarchy below, MDG-F supports the 3 main areas in financial accounting, i.e. Accounting, Controlling and Consolidation.
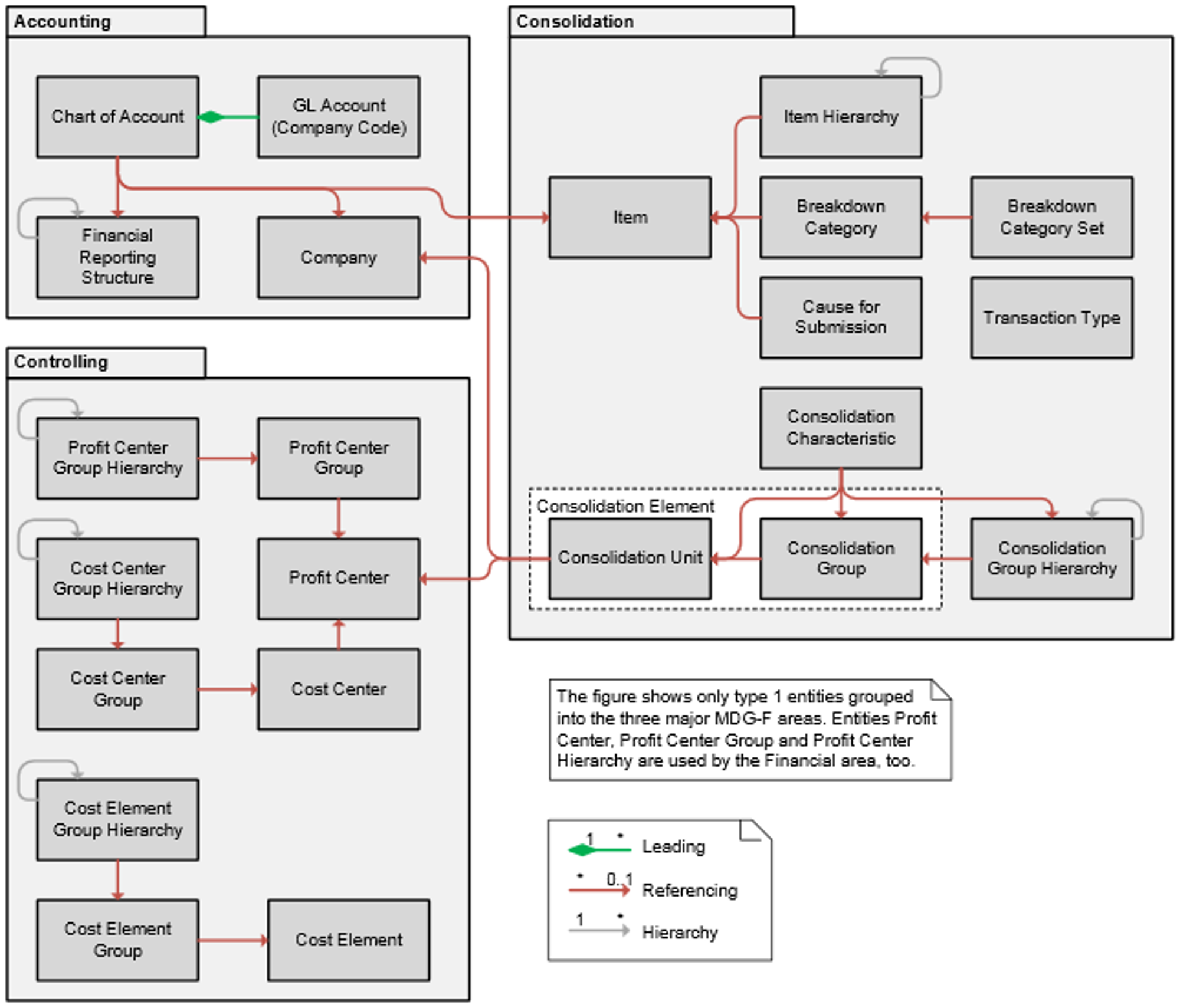
Because all entities in this hierarchy are linked, it becomes more complicated to create incoherent or inconsistent data. A web of aligned and linked master data is created, as it were.
Various validation options can be used so that only allowed and correct content is managed. SAP MDG-F also offers the possibility of storing draft versions of master data or incomplete records that do not yet meet all validation requirements. However, before final approval can be given, all validation requirements should comply, to avoid incorrect or incomplete data in the underlying business systems.
Editions
Usually, time-dependent checks on master data release are not taken into account in master data processes. Within MDG-F, however, this is standard, because of the so-called Editions (or versions). All change requests within MDG-F, also for new objects, are collected in one edition and released on a specific date. Time-dependent objects automatically receive their validity from the validity data of the parent edition. After an edition is released, all change requests in the edition are only made available to the underlying systems. Furthermore, an edition can only be released when all change requests in the edition have been completed; i.e. approved, rejected, or cancelled. When the edition is released, a validation is performed for all change requests in the edition. If any inconsistency is found, the edition cannot be released and the errors that appear must be resolved first. In this way, MDG-F ensures that only consistent and correct input of master data to the linked operating systems takes place.
When an edition is created, MDG-F automatically determines the date from/till when the edition is valid, based on existing editions. In this way, there can be no overlap between different editions. An edition can only be valid till the validity of a new edition.
By way of illustration:
- Edition A is valid from 01/2019 till 12/9999
- When edition B is created valid as of 11/2018, then MDG-F automatically will adjust the ‘validity to’ for edition B to 12/2018.
- Edition A is valid from 01/2019 till 12/9999
- When edition B is created valid as of 11/2020, MDG-F automatically will modify the validity of edition A from 01/2019 till 10/2020.
Change requests within MDG-F always fall within one edition, no matter whether the change has to be implemented directly in the underlying business systems or later on. This is because it is possible to implement changes within an edition in underlying business systems, without the edition having been released. In this way, small independent changes can be implemented, without having to release the entire edition.
When the change request is created, the choice must be made in which edition the change should be included and so in which time period the changes become active. It is possible to choose an edition that is valid today, in order to be able to implement changes immediately or to choose an edition that is only valid later to schedule future changes. As soon as an edition becomes active, i.e. the current date falls in the validity of the edition, all changes in the edition can be implemented to the underlying business systems. Of course, in all cases, all validation checks and approvals have to be done.
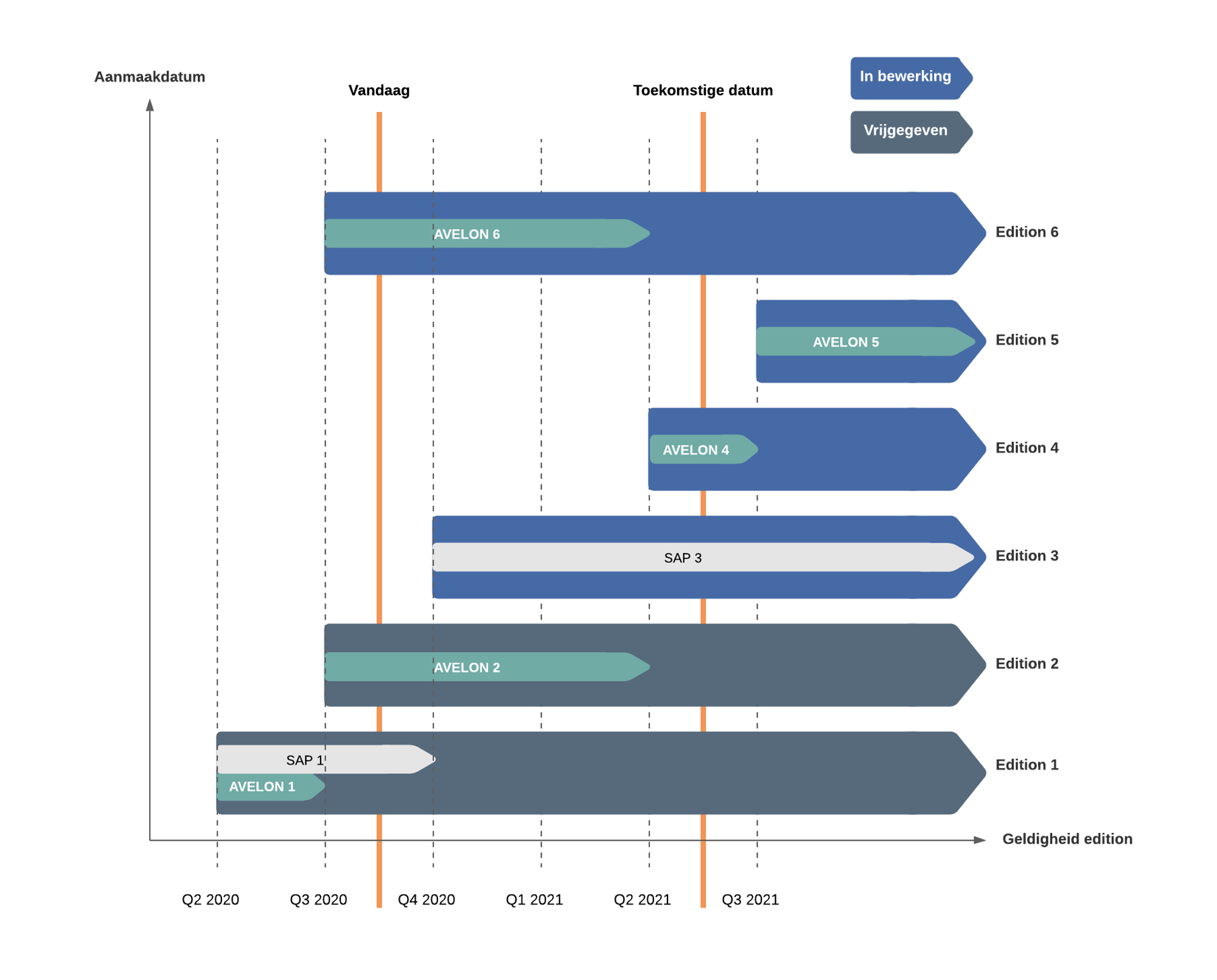
In the above diagram, the changes on two cost centres are illustrated: cost centre AVELON and cost centre SAP. Looking at the cost center AVELON, we can conclude:
- In Q2 of 2020, version AVELON 1 was valid in released Edition 1.
- From Q3 2020, version AVELON 2 becomes active from the released Edition 2.
- Also, for changes in Q3 2020, a new Edition 6 has been created, which is still in progress. In Edition 6, changes are included in version AVELON 6 in comparison with AVELON 2.
- From Q2 2021, version AVELON 4 becomes active from Edition 4, valid until Q3 2021.
- From Q3 2021, version AVELON5 becomes active from Edition 5, valid until Q4 9999.
- On the date "Today", versions AVELON 2 and AVELON 6 are active. AVELON 2 is already in the released edition, but has to be changed. A new edition has been created to include changes to AVELON 2 and this becomes AVELON 6.
- On the date "Future date", version AVELON 4 becomes active.
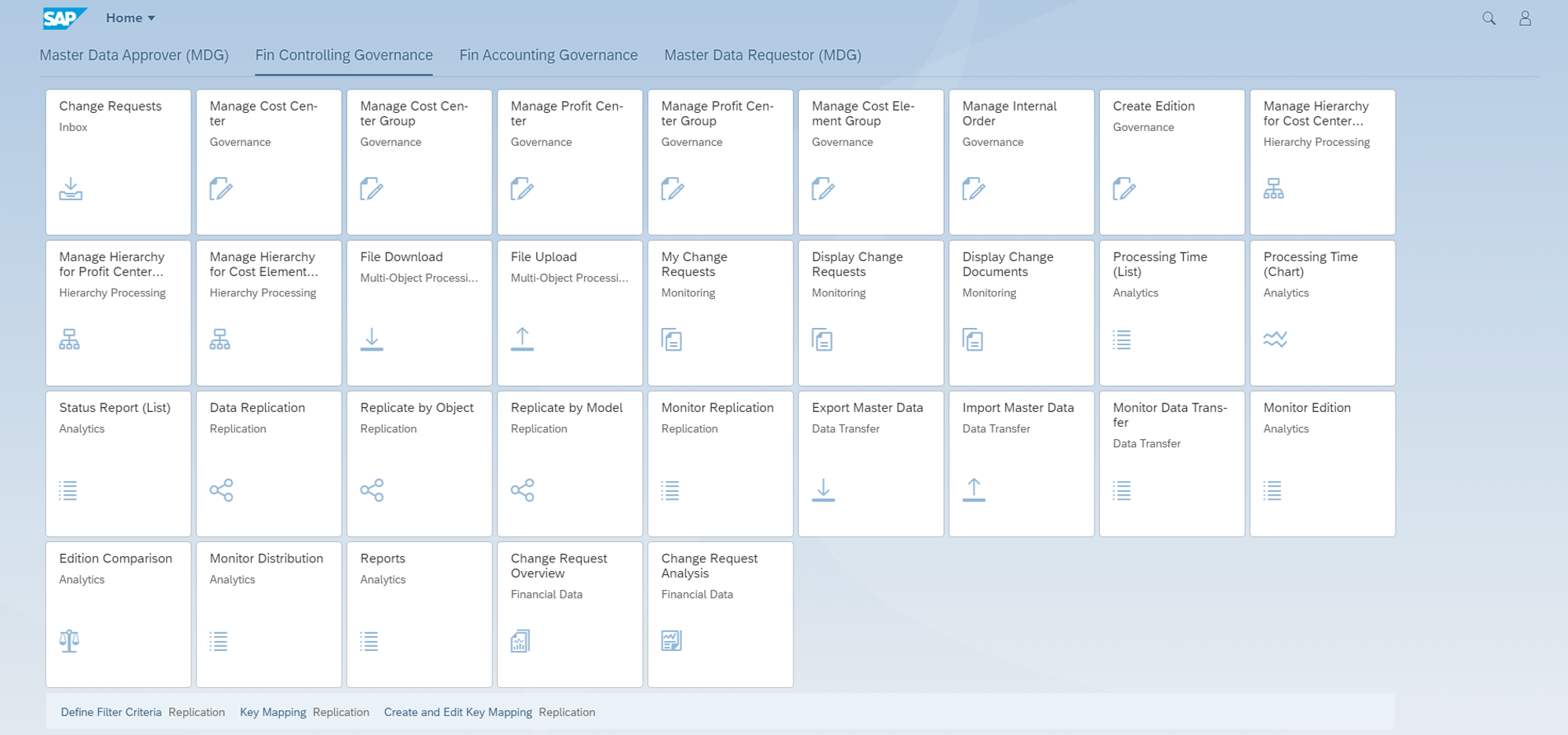
SAP Fiori
SAP MDG-F, just like the other MDG domains, is provided with a wide range of Fiori applications, which facilitates an intuitive and smooth user experience.
Requesting financial master data, for example, can easily be provided via a Fiori application, in which it is not yet necessary to fill in all the required information.
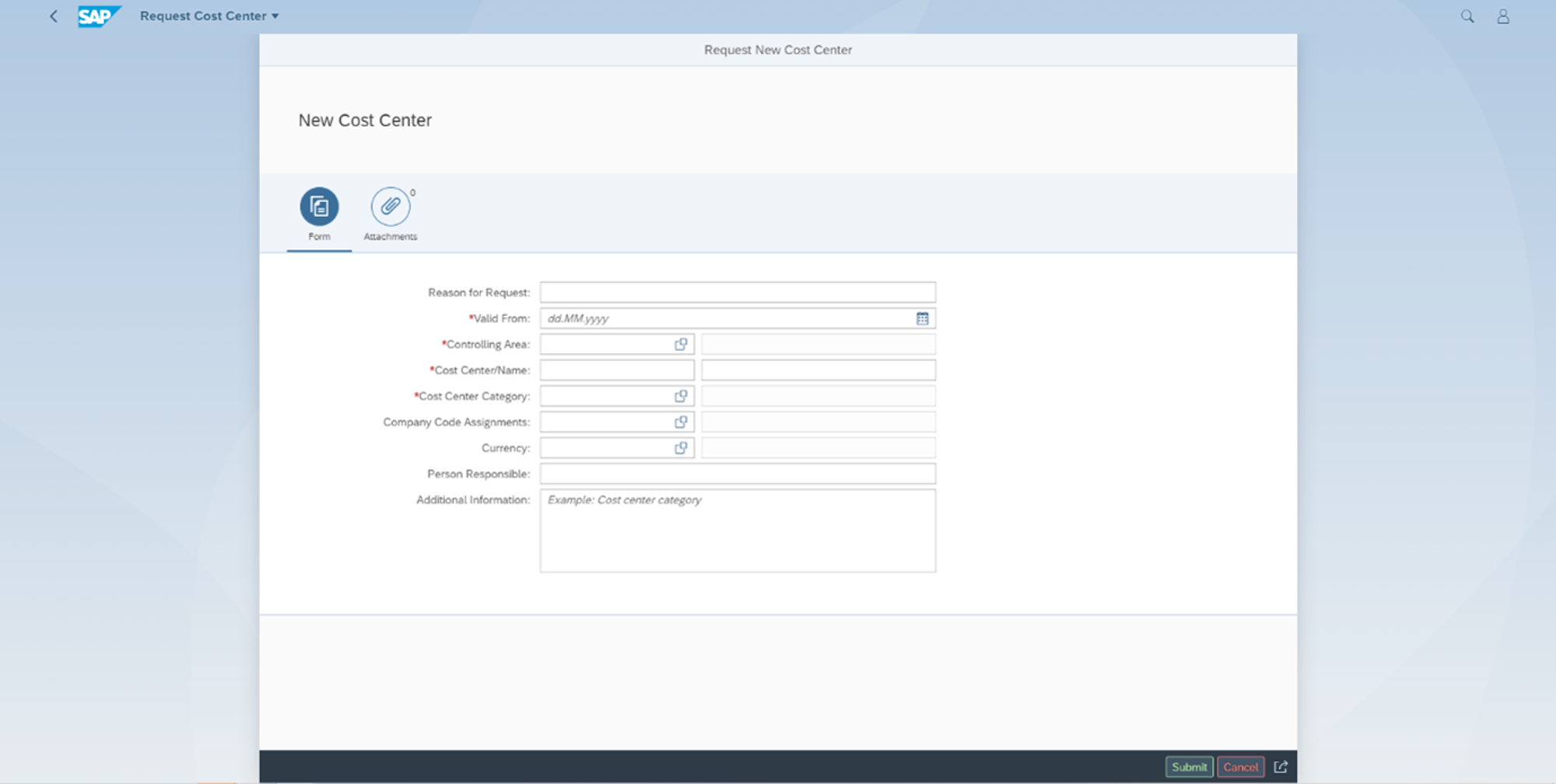
Missing data can later be supplemented by a master data specialist in another Fiori application. Subsequently, the requested and completed master data can be approved in yet another Fiori application.
Next to SAP Fiori applications for guiding the process for change requests related to financial master data, SAP MDG-F also has the so-called Fiori Analytics applications. Via various Fiori reports, insight can be given in into the SAP MDG-F processes.
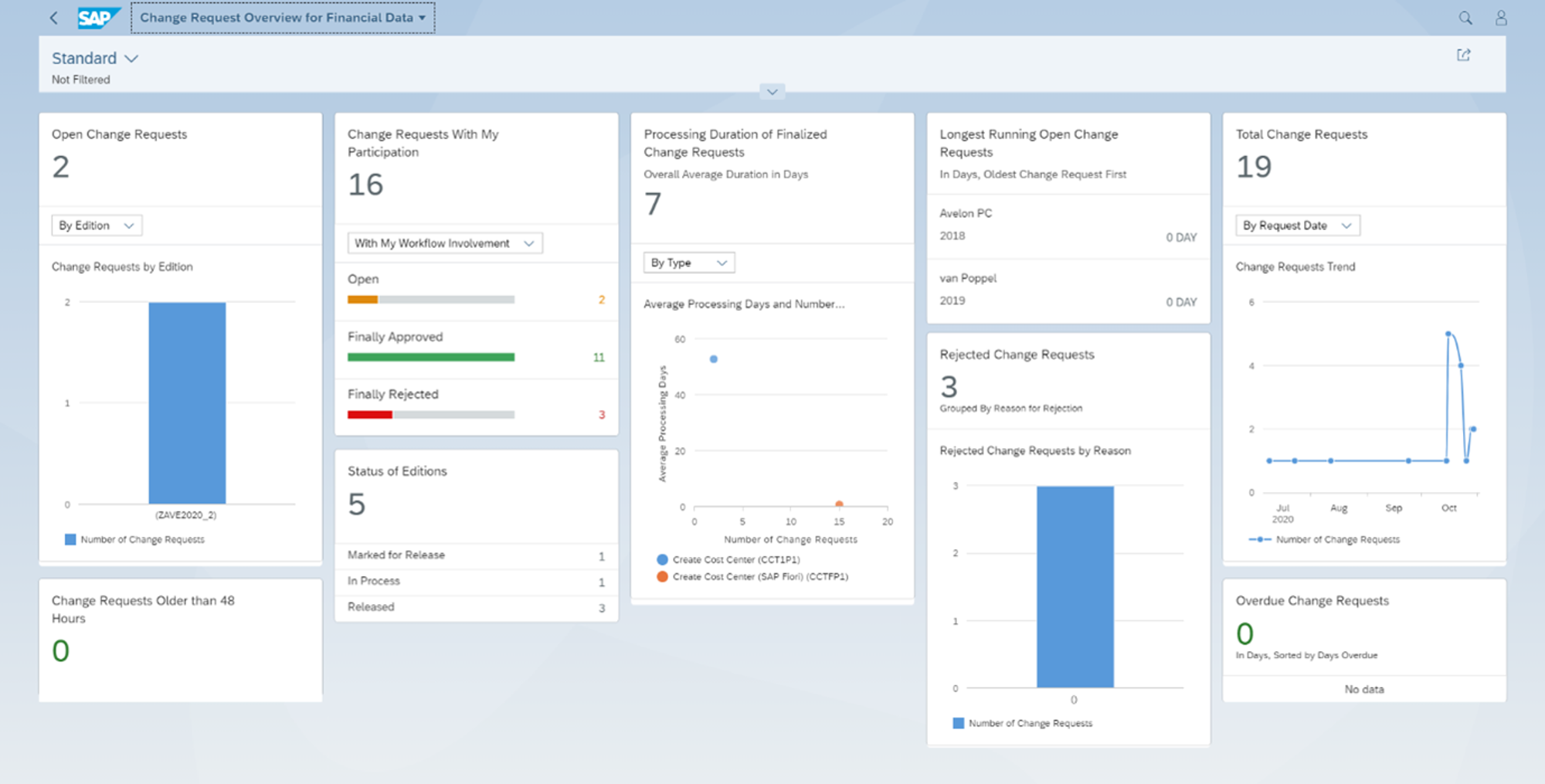
Demo
The video below runs through a scenario in which a new cost center is requested on a S/4HANA MDG 1909 system.
Conclusion MDG-F
MDG-F provides you with an application that optimizes your financial master data and allows you to manage financial data within your company through streamlined processes.
In a nutshell, MDG-F facilitates:
- consistent financial master data throughout the organization;
- traceability changes for regulatory requirements;
- optimization of financial processes, internal audits, short cycle times for closing periods;
- high quality of the financial master data. Data is reliable, with only one version of the truth;
- import of business data from external systems, such as investment management systems;
- through Fiori applications, MDG-F offers a user-friendly user interface for managing master data and handling change requests;
- no duplicated data in the SAP system;
- time-dependent and period-based versions of master data through editions.
For further information on this subject, please fill in the form below. An expert will get in touch soon.

Wouter Van Peteghem
Managing Partner
With 23 years of experience in SAP, Wouter is now responsible for business development, HR and daily operations at Alluvion.
Featured articles