Introduction
As enterprises head towards their transformative journeys, the integration and governance of data become more and more important. SAP Master Data Governance should emerge as a key player in this scenario, especially in projects involving RISE with SAP and SAP S/4HANA transformations, yet is often overlooked. Good Master Data Management ensures the highest quality and consistency of master data, aligning perfectly with the objectives of these comprehensive digital transformation frameworks, especially in the age of AI. This blog delves into the strategic importance of SAP MDG in enhancing your MDM processes during these transformation initiatives.

Understanding the Need for SAP MDG
In today's data-driven business landscape, the management of master data is not just a technical necessity but also a strategic approach. Master data contains all critical business entities such as products, suppliers, customers, business partners and financial information, which are used in nearly all enterprise operations. Its role becomes even more important in the context of major transformation projects like RISE with SAP, SAP S/4HANA on-premise and Public Cloud.
The integration of SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) addresses a shift to SAP S/4HANA or adopting the RISE with SAP model, the quality and consistency of master data directly impact the success of their digital transformation efforts. SAP MDG steps in as a tool that can ensure data migrating into new systems is not only accurate but harmonized across various business units.
Without SAP MDG, organizations risk data inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and inefficiencies that can disrupt business processes, decision-making, and compliance efforts. By standardizing and streamlining data governance, SAP MDG helps enterprises to maintain data integrity, which is crucial for achieving the insight, and operational efficiency that are the goals of digital transformation initiatives.
The strategic deployment of SAP MDG, therefore, is not just about maintaining and elevating data quality; it's about empowering businesses to leverage their data as a strategic asset, ensuring that as they transform with RISE with SAP or S/4HANA, their data governance framework is robust, compliant, and capable of supporting their evolving business needs.
Challenges in Integrating SAP MDG
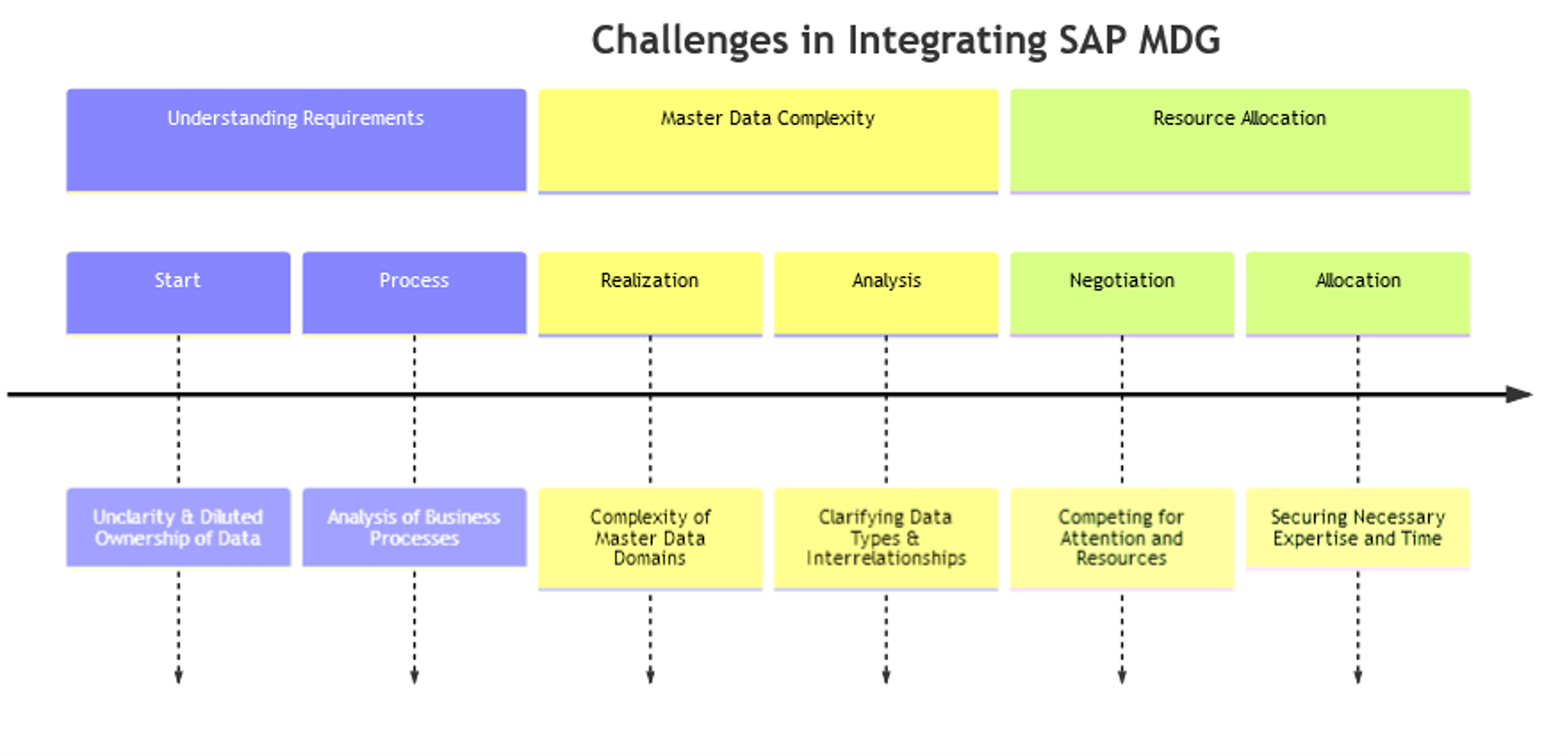
Unclarity & diluted ownership of Data
The initial challenge is closely linked to understanding all the necessary configuration requirements for an MDG implementation. This process involves a thorough analysis of existing business processes to determine how they interact with different master data elements. Often, process managers may not fully comprehend their master data needs, leading to gaps in the MDG design. Bridging this gap needs a methodical approach, involving stakeholders across the organization to ensure that all master data requirements are comprehensively identified and appropriately addressed, which creates heavy business involvement.
The Complexity of the Master Data domains
The next challenge in integrating SAP MDG into RISE with SAP and S/4HANA projects lies in comprehending the diverse and complex nature of master data. Master data spans various domains with each its unique characteristics and importance. However, the complexity is further amplified when custom fields or entities specific to your organization come into play. Achieving clarity on these data types and understanding their interrelationships within the S/4HANA environment is critical, requiring not only technical acumen but also a deep understanding of how master data underpins key business processes. So, this also shows the need to have a clear and thorough analysis of your current master data processes before stepping into the project. Of course, this is something your implementation partner can and should help with, but this again requires assistance from the business.
People and Budget Allocation
Another significant hurdle is that, while mentioned already above, the necessary people should be allocated to the MDG project. Master data management often competes for attention and the availability of business with other major initiatives, such as the broader S/4HANA transformation. Ensuring that knowledgeable personnel are available and can dedicate sufficient time to the MDG workshop, blueprint and analysis part of the MDG project. This often means negotiating within the larger scope of the S/4HANA project to secure the necessary resources and expertise, a task that can be challenging given the typical prioritization of transformation objectives over data governance in the planning stages.
Mitigation Strategies
Approach to Methodology
Overcoming challenges in method analysis and data model development often demands outside expertise. Firms specializing in SAP MDG bring systematic methods for capturing requirements and imparting these methodologies across project teams. Adopting these proven strategies and tailoring interactive workshops can lead to a more effective MDG design and implementation, smoothing the way through common obstacles.
Emphasizing Collaboration
The cornerstone of MDG project success is building a collaborative atmosphere. Engaging representatives from different departments through frequent workshops and forming teams allows the promotion of a mutual understanding of master data necessities. This cooperative effort ensures that master data requisites of each business unit are acknowledged and incorporated into the MDG plan. It also aligns MDG goals with wider objectives of the S/4HANA transition and RISE with SAP programs, embedding master data management within the broader organizational transformation.
Promotion and Sponsorship
Addressing SAP MDG integration challenges starts with a solid business justification and securing top-level support. Highlighting MDG’s benefits, like cost reduction and improved operational efficiency, can win over key organization leaders. This backing is crucial during the phases of prioritizing and allocating business staff, as discussed earlier. Converting MDG technical jargon into a business glossary familiar within the organization fosters common understanding and aligns various departments with the MDG endeavour. It also eases future onboarding processes due to the availability of a cross-departmental business glossary.
Proactive outreach is essential. Engaging with key stakeholders in S/4HANA and RISE with SAP projects, including leads in procurement, sales, logistics, or business architecture, is vital. Demonstrating MDG's direct impact on their master data areas through practical examples can secure their endorsement. Additionally, connecting with potential line of business users in the organization to share the MDG project's vision and benefits is key in identifying enthusiastic project supporters and experts.
Strategic Advantages of SAP MDG Integration
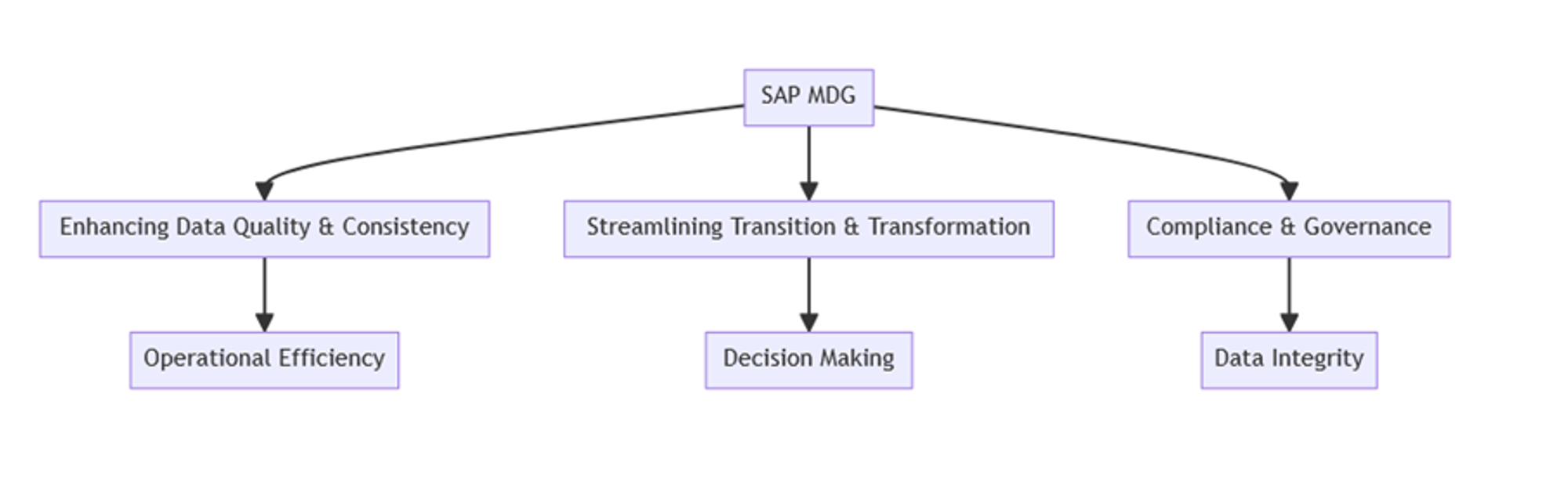
Enhancing Data Quality and Consistency
One of the most significant advantages of integrating SAP MDG in RISE with SAP and S/4HANA projects is the substantial improvement in data quality and consistency. SAP MDG acts as a central hub for managing master data across the enterprise, ensuring that data migrating to new systems is accurate and consistent. This capability is particularly important during the transition to SAP S/4HANA, where the integrity of data directly influences the performance and reliability of the new system. By eliminating duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing data formats, SAP MDG makes a pivotal contribution to the operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities of the organization.
Streamlining Transition and Transformation
Integrating SAP MDG into these transformation projects strategically aligns master data management with the overall transformation goals. This alignment allows for a smoother transition to SAP S/4HANA and RISE with SAP by addressing data issues upfront before the migration. By dealing with data quality and governance in tandem with the system migration, organizations can avoid the complexities of retrofitting these elements later, leading to more efficient implementation and reducing the time to value for the new systems.
Compliance and Governance
Another critical advantage is the enhancement of governance and compliance. SAP MDG provides a framework for data governance, ensuring adherence to internal and external policies and regulations. This is increasingly important in a landscape where data privacy and compliance are needed. The transparency and control offered by SAP MDG enable organizations to manage their data with greater accountability, ensuring high levels of data integrity and trust.
Conclusion
In summary, the integration of SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) in both RISE with SAP and SAP S/4HANA transformation projects is a strategic decision that goes beyond a mere technical implementation. It represents the organization’s commitment to data quality, data integrity, operational efficiency, and compliance which are key pillars of successful digital transformation. By enhancing data quality, streamlining transitions, and ensuring governance, SAP MDG allows organizations to fully leverage their investment in SAP systems. As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, the role of SAP MDG as a facilitator of reliable, efficient, and compliant data management becomes increasingly indispensable. This integration is not just an upgrade; it's a foundational step towards future-proofing an organization's data landscape, especially in times like this where AI solutions are popping up all over the world. Guess what’s driving AI?
Data!
Want more information? Fill in the form below, and one of our experts will be in touch soon!

Nicholas Vermeersch
Business Developer
Project Manager and Senior SAP Master data consultant specialized in SAP Master Data
Governance (MDG) and good overall knowledge of the SAP NetWeaver concept.
Featured articles